Mesoscale Model of Chloride transport in concrete
Computational Mechanics of Soft Materials Lab
When reinforced concrete structures are located in coastal areas or regions where salt is used to de-ice roads, they are regularly subjected to chloride attacks. This shortens the lifespan of such structures as the migration of chlorides can cause rapid corrosion when they make contact with the steel rebar embedded in the concrete.

corroded embedded rebar
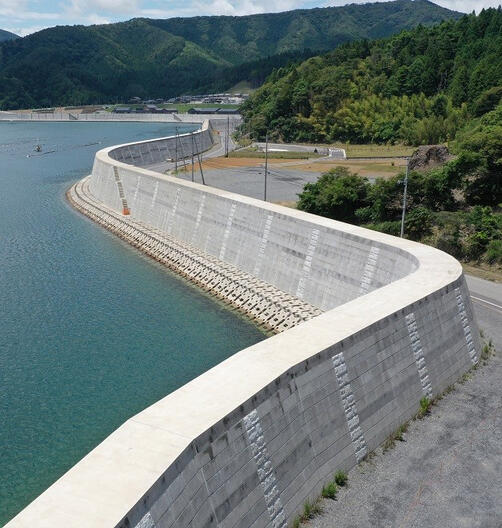

tsunami wall in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan
By creating a chloride transport model for concrete, we hope to find ways to slow down the diffusion of chloride throughout concrete. Doing so can allow us to develop higher performance concretes that will better protect rebar from chloride and increase the lifespan of reinforced concrete structures.
Creation And Model Components
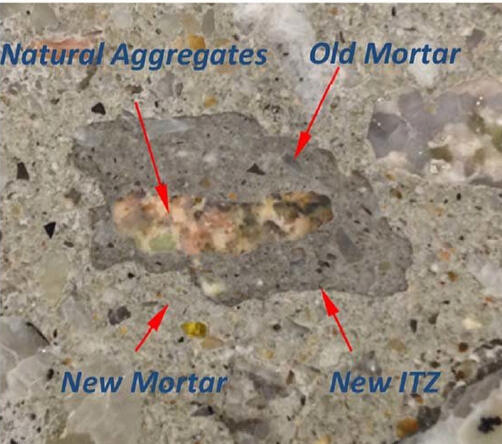

sliced concrete with labelled parts
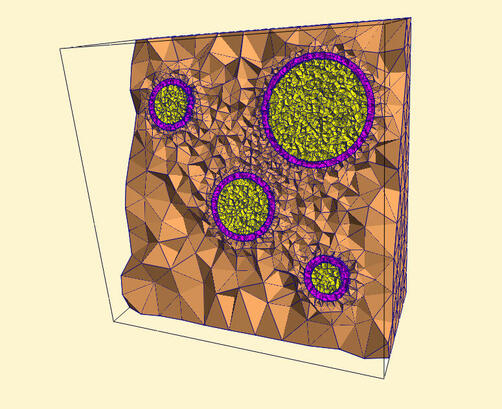
meshed concrete model
The following three components are considered in our chloride transport model
- Course Aggregate- Interfacial Transition Zone (ITZ)- Mortar
All three parts of the model were meshed using Gmsh with local mesh refinement being performed where the Interfacial Transition Zone makes contact with the mortar
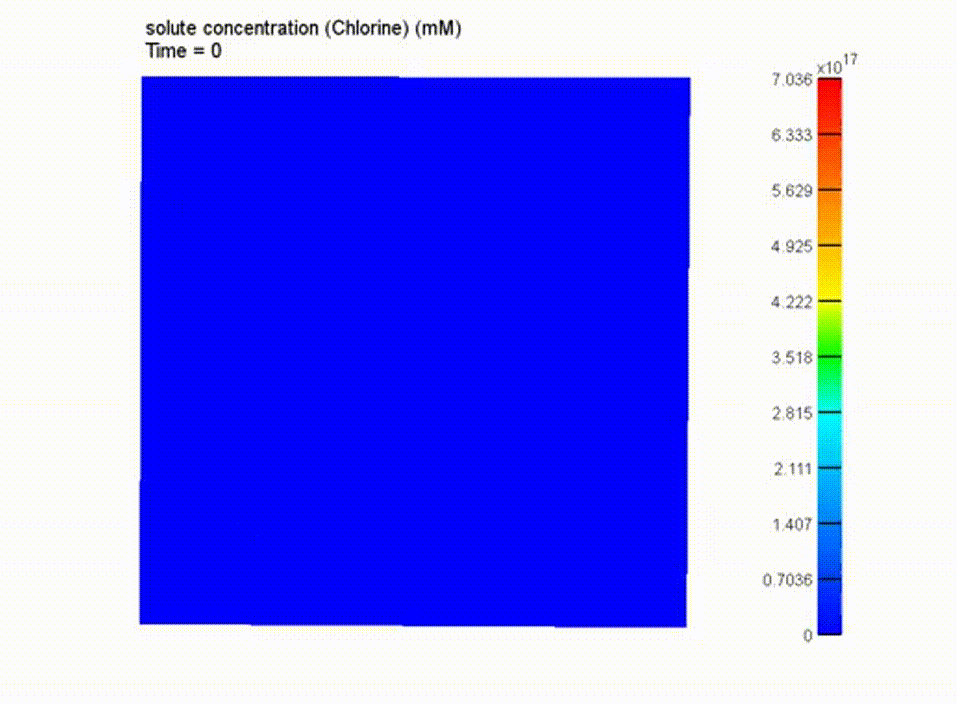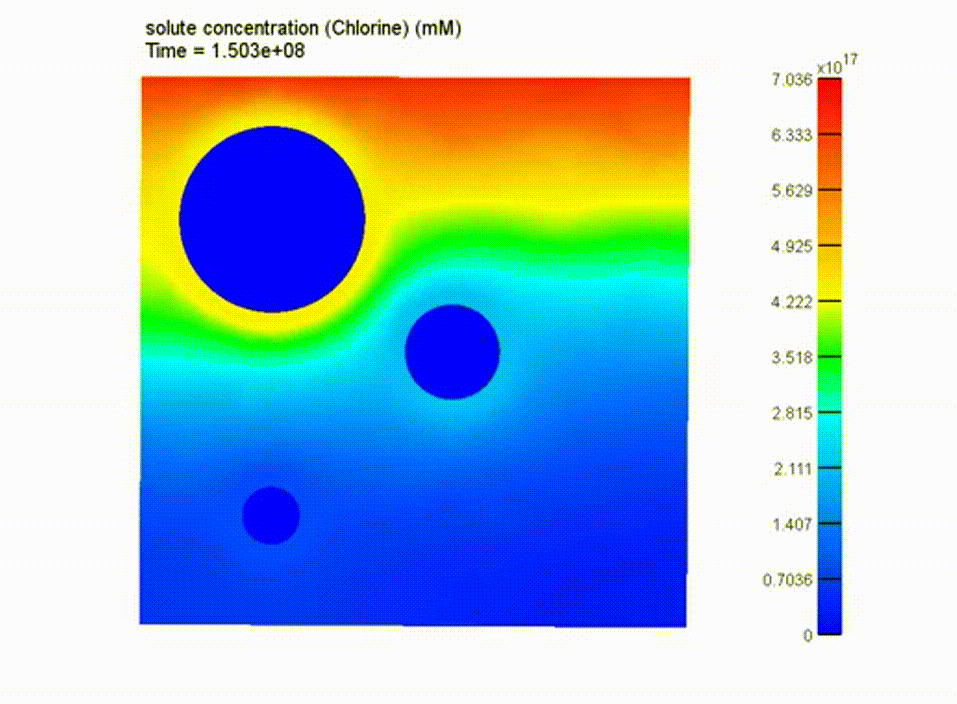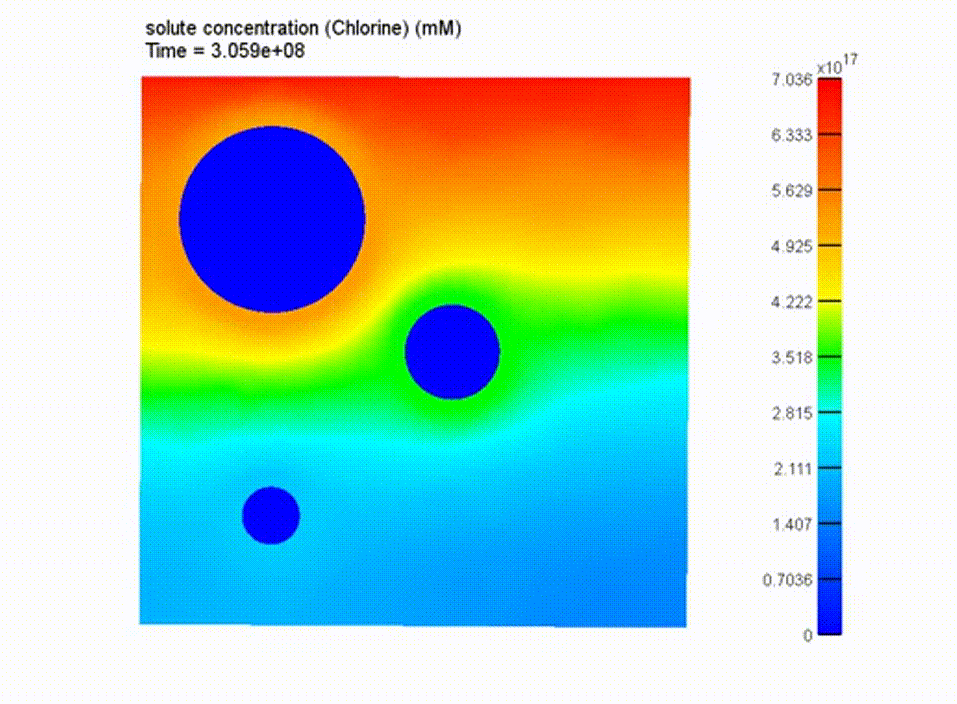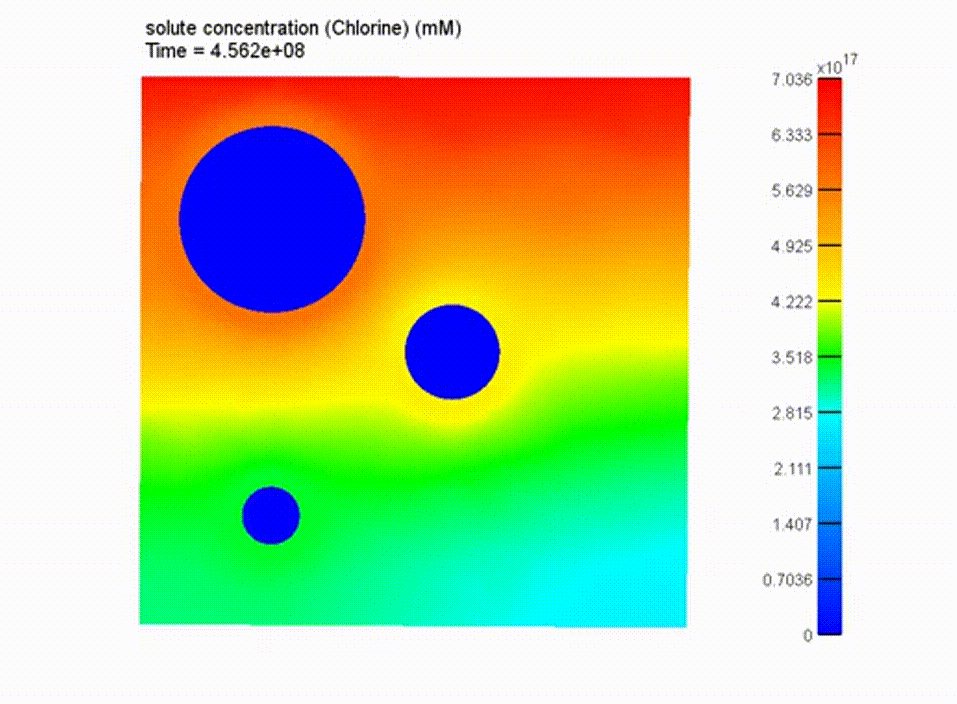
Boundary Conditions and Results
boundary conditions applied to model

cross-sectioned chloride transport results